BlueZone partners with over 50
world-leading original equipment
manufacturers and systems providers
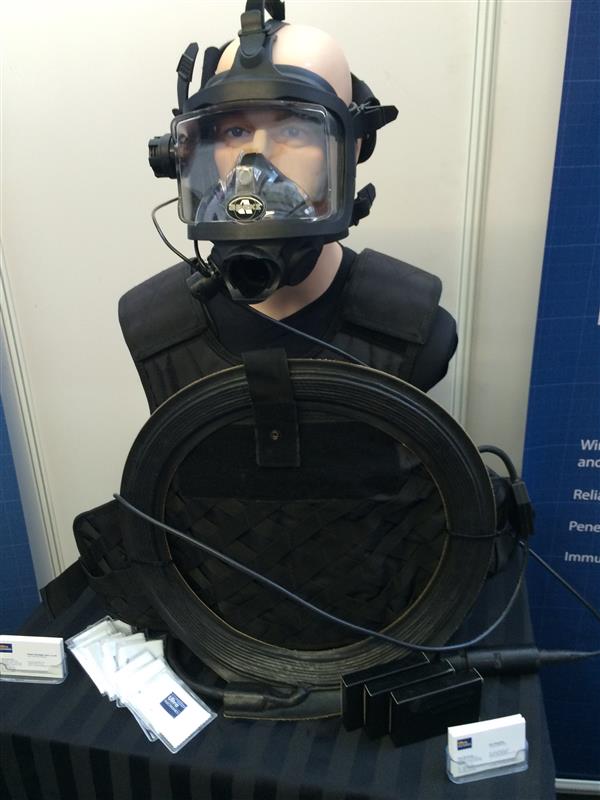
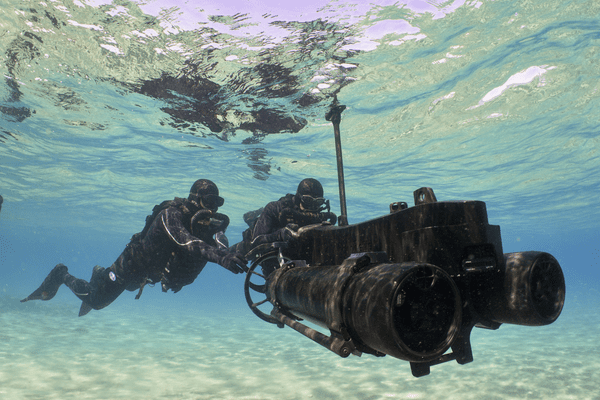
DiverCOMM
DiverCOMM is a lightweight, tactical, voice communications system using Magneto-Inductive (MI) signalling technology. Unlike radio frequency (RF) and acoustic signals, the low frequency MI signal can penetrate through air-water boundaries, providing users with secure and reliable connectivity in most acoustically challenging environments. The Magneto-Inductive (MI) signalling does not propagate like RF or acoustic signals and is virtually undetectable.
DiverCOMM operates in both air and water, enabling a diver in the water to talk to a supervisor directly. For operations such as a hull search, divers on hull search can talk to each other and relay messages via last diver to surface. DiverCOMM is immune from acoustic interference and so will provide an unprecedented communications capability in noisy harbours or industrial locations where commercial divers are often required to operate.
Key Features
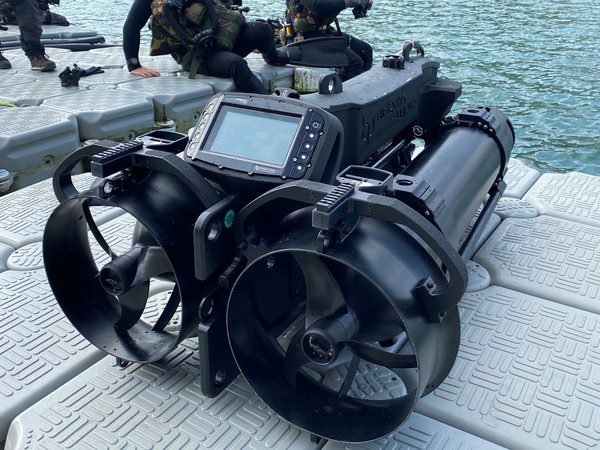
Up to 25-hour mission duration
Speeds up to 4.2 knots
Increased module payload capacity
Search and recovery
Hydrography
Deep sea mineral exploration
Marine & Fisheries research
Product Enquiry
Related products
The DPR-275 Diver Pinger Receiver is a small and rugged handheld diver acoustic receiver with an LCD display and signal strength meter that can track and locate any acoustic pinger...
Read moreBlueprint Artemis Diver Navigation Systems
The Blueprint Artemis range consists of four diver navigation systems
Read moreSUEX Diver Propulsion Vehicle - The Submarine Exploration Company - represents the cutting-edge technology of underwater mobility.
Read moreRelated Articles
Expanding Horizons: MARVEL Micro-AUV Joins the SEABER Family
Unveiling Cutting-Edge Capabilities SEABER recently unveiled the newest addition to its cutting-edge range with the MARVEL micro-AUV. The MARVEL is setting a new standard in precision underwater exploration. The new...
Read MoreHII Mission Technologies Newest Addition: The REMUS 130 UUV
Open Architecture and Modularity Minimize Cost and Risk HII announced the newest third generation REMUS 130 unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV), which is based on the highly successful REMUS UUV series....
Read MoreSEABER YUCO-SCAN micro-AUV Demonstration
Exploring the Future of Underwater Surveys. On the 5th of February 2024, BlueZone Group successfully completed the first demonstration with the SEABER YUCO-SCAN micro-AUV at Lake Macquarie, NSW. This demonstration...
Read More